Trial and Error Learning: The famous psychologist Edward Lee Thorndike (1834 – 1949) was the initiator of the theory of trial and error learning based on the findings of his experiment on cats.
For example, in one of his experiments, he placed a hungry cat in a puzzle box. There was only one door that could be opened by operating a mechanism correctly. There was a fish kept outside the box.
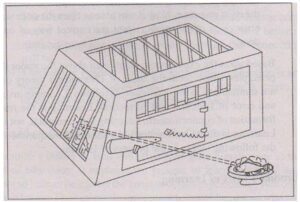
The smell of the fish ached as a strong motive for the hungry cat to come out of the box.
In another test, the process was repeated. The cat was kept hungry and placed in the same place in the same puzzle box. The fish and its smell again induced him to get out of the box, he again made disorderly movements and frantic efforts. But this time it took less time to come out. In subsequent trials, such incorrect responses as biting, clawing, and lashing gradually decreased and the cat took less time on each successful trial. Over time, this came to be in a position to manipulate the latch as soon as it was inserted into the box. In this way the cat gradually learned the art of opening the door. The experiment summarizes the following steps in the learning process.
| 1 | Drive | In the present experiment it was hungry and was intensified by the sight of the food. |
| 2 | Goal | To get at the food by getting out of the box. |
| 3. | Block | The cat was confined in the box with a closed door. |
| 4 | Random Movements | The cat persistently tried to come out of the box without knowing how. |
| 5 | Selection | Gradually, the cat recognized the correct way to manipulate the latch. It selected the proper way of manipulating the latch out of its random movements. |
| 6 | Fixation | At last, the cat learned the proper way to open the door by eliminating all the incorrect responses and fixing only the right response. Now it was able to open the door without any error or in other words, learnt the correct way of opening the door. |
Based on the experiment mentioned above the major theoretical principles that form the basis of Thorndike’s learning theory and discussed briefly are as follows. Learning involves trial and error or selection and improvement. Learning is the result of building relationalism. Learning is incremental, not practical; Learning is direct, not mediated by thoughts. The experiment summarizes the following steps in the learning process.